Contents
- 1 Understanding Diabetes and Its Complications
- 2 Recognizing the Signs of Diabetic Foot Problems
- 3 Importance of Regular Foot Care
- 4 How Diet Impacts Diabetes Management
- 5 The Role of Exercise in Prevention
- 6 Seeking Professional Medical Help
- 7 Conclusion
- 8 FAQ – Common Questions About Diabetes Management
- 8.1 What are the signs that I should watch for regarding diabetic foot problems?
- 8.2 How can a healthy diet help manage diabetes?
- 8.3 What types of exercise are beneficial for diabetes management?
- 8.4 Why is regular foot care important for diabetics?
- 8.5 How often should I see my healthcare provider for diabetes management?
- 8.6 What should I do if I have a foot injury as a diabetic?
Effectively managing diabetes is essential to prevent serious complications like amputations. Key strategies include understanding the disease and its risks, recognizing early signs of foot problems, maintaining regular foot care, following a healthy diet, engaging in consistent exercise, and seeking professional medical help when needed. By implementing these proactive measures and monitoring your health regularly, you can significantly enhance your diabetes management and overall quality of life.
Curious about preventing diabetes-related amputations? It’s a crucial topic, especially for those living with diabetes.
The unfortunate reality is that diabetes can lead to severe complications, including amputations, if not managed properly.
But the good news is that with proactive measures, many of these complications can be prevented.
In this article, we’ll delve into essential strategies to protect your limbs and overall health, covering everything from proper foot care to lifestyle changes that make a big difference.
Understanding Diabetes and Its Complications
Understanding diabetes is crucial for anyone looking to prevent its complications. Essentially, diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how your body processes blood sugar (glucose). When your body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or becomes resistant to it, glucose builds up in the bloodstream, leading to a range of health issues.
There are two main types of diabetes: Type 1 and Type 2. Type 1 diabetes, usually diagnosed in children and young adults, occurs when the body doesn’t produce insulin at all. On the other hand, Type 2 diabetes, which is more common, generally develops in adults and is often associated with obesity and lifestyle choices.
Now, here’s where it gets serious—if diabetes isn’t managed effectively, it can lead to several complications. High blood sugar levels over time can damage blood vessels and nerves, particularly in your feet. This nerve damage can result in peripheral neuropathy, meaning you may not feel cuts or sores on your feet, putting you at risk.
Some other common complications include:
- Cardiovascular disease: Diabetics are at a higher risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- Kidney damage: High blood sugar can affect your kidneys’ ability to filter waste.
- Eye damage: Diabetes can lead to diabetic retinopathy, which affects vision.
- Foot damage: Poor circulation and nerve damage can lead to infections and, in severe cases, amputations.
Understanding these complications is the first step towards prevention. Being aware of the risks associated with diabetes empowers you to take proactive measures. Regular check-ups, proper medication adherence, and lifestyle modifications can significantly lower your chances of developing these serious complications.
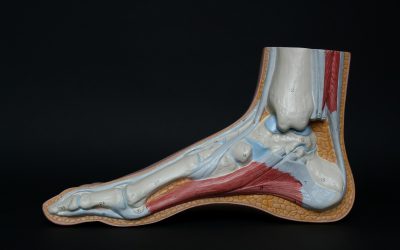
Recognizing the Signs of Diabetic Foot Problems
Recognizing the signs of diabetic foot problems is essential for preventing severe complications, including amputations. Since diabetes can cause nerve damage, also known as neuropathy, you might not feel injuries on your feet—making regular inspections all the more vital. Here are some key signs to watch for:
1. Numbness or Tingling: If you experience a loss of feeling, tingling, or a ‘pins and needles’ sensation in your feet, it could be a sign of nerve damage. This lack of sensation can prevent you from noticing cuts or sores.
2. Sores or Wounds: Look for any blisters, cuts, or wounds that do not heal properly. A simple blister can become infected if left untreated, leading to more serious issues.
3. Redness or Swelling: Any unusual redness or swelling on your feet can indicate an infection or inflammation. This is particularly concerning if it’s accompanied by warmth or pus.
4. Calluses or Corns: Thickened areas on your feet can develop if your weight distribution is uneven due to neuropathy. These calluses can crack and become entry points for infections.
5. Changes in Skin Color or Texture: Monitor for changes in skin color—such as patches of darkened or shiny skin—as these alterations may indicate poor circulation.
6. Foul Odor: An unusual smell can signal an infection. If you detect any foul odor coming from your feet, it’s time to seek medical attention.
Remember, early detection is key! Regularly inspect your feet at home, and if you notice any of these signs, consult your healthcare provider promptly. A proactive approach can prevent minor issues from escalating into serious complications.
Importance of Regular Foot Care
The importance of regular foot care cannot be overstated for individuals with diabetes. Taking care of your feet is one of the most effective ways to prevent complications, including infections and, in severe cases, amputations. Here’s why it matters:
1. Prevention of Issues: Daily foot care helps in identifying problems early. Inspecting your feet for cuts, blisters, or redness can catch issues before they become serious. Remember, early intervention is key!
2. Maintaining Skin Health: Keeping your feet clean and moisturized can prevent dry skin and cracking. Diabetics are at a higher risk for skin problems, so a simple daily routine of washing and moisturizing your feet can go a long way.
3. Proper Nail Care: Gently trimming your toenails straight across can prevent ingrown nails, which can lead to infections. If you’re unsure how to do this safely, don’t hesitate to ask a healthcare professional for guidance.
4. Footwear Matters: Choosing the right shoes is crucial. Properly fitted shoes provide support and reduce the risk of pressure sores. Avoid tight or poorly fitting footwear that can lead to blisters and calluses.
5. Professional Assessments: Regular visits to a podiatrist (foot specialist) are essential. They can perform thorough examinations of your feet, offer specific care tips, and detect problems that you might not notice.
6. Building Awareness: Incorporating foot care into your daily routine reinforces the importance of self-monitoring. When you take time to care for your feet, you’re more likely to stay alert to any changes, making it easier to spot potential issues.
In conclusion, regular foot care isn’t just about keeping your feet looking good—it’s a vital part of your overall health management. By prioritizing foot care, you can significantly reduce your risk of complications stemming from diabetes, keeping your feet healthy and your body active.
How Diet Impacts Diabetes Management
Your diet plays a crucial role in managing diabetes. What you eat can directly influence your blood sugar levels, and making informed dietary choices is essential for your overall health. Here’s how diet impacts diabetes management:
1. Blood Sugar Control: Foods high in refined sugars and carbohydrates can cause spikes in blood sugar levels. By focusing on low glycemic index (GI) foods—like whole grains, legumes, and non-starchy vegetables—you can help maintain steadier blood sugar levels throughout the day.
2. Portion Control: Managing portion sizes is essential. Eating excessive amounts of food, even if it’s healthy, can lead to increased blood sugar levels. It’s important to pay attention to serving sizes and to eat balanced meals comprised of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates.
3. Nutrient Density: A well-rounded diet rich in vitamins and minerals can support your overall health. Foods like leafy greens, fruits, lean proteins, and healthy fats should be staples in your diet. They not only help in managing diabetes but also strengthen your immune system.
4. Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight helps improve insulin sensitivity. A diet focusing on whole foods, higher in fiber but lower in saturated fats, can aid in weight loss or maintenance—both of which are vital for managing Type 2 diabetes.
5. Staying Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water is often overlooked in diabetes management. Staying hydrated helps your kidneys flush out excess sugar through urine. Aim for at least eight glasses of water a day, and reduce sugary drinks that can spike blood sugar levels.
6. Meal Timing: When you eat can be just as important as what you eat. Regular, balanced meals help regulate blood sugar levels. Try to eat at the same times each day to maintain consistency in your body’s insulin response.
Ultimately, a balanced diet tailored to your specific needs can have a profound impact on your diabetes management. Consulting with a registered dietitian can provide personalized meal plans and further guidance on food choices that best support your health and lifestyle.
The Role of Exercise in Prevention
Exercise plays a vital role in the prevention of diabetes-related complications, making it an essential part of managing diabetes. Regular physical activity not only helps control blood sugar levels but also offers numerous health benefits. Here’s a closer look at how exercise can aid in prevention:
1. Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Engaging in regular physical activity helps your body use insulin more effectively. When you exercise, your body becomes more sensitive to insulin, which helps lower blood sugar levels—essential for diabetes management.
2. Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for diabetes control. Exercise burns calories and helps maintain or lose weight, which can significantly improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes.
3. Cardiovascular Health: Diabetes increases the risk of heart disease. Regular aerobic exercise strengthens your heart and improves circulation, helping lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
4. Enhanced Mood and Mental Health: Physical activity releases endorphins, the body’s natural feel-good hormones. This can help combat stress, anxiety, and depression—conditions often experienced by those with chronic illnesses. Improved mental well-being makes it easier to stay committed to a healthy lifestyle.
5. Better Blood Sugar Control: Exercise naturally lowers blood sugar levels during and after activity. Engaging in both aerobic and resistance training improves your body’s ability to regulate blood sugar, further minimizing the risk of complications.
6. Increased Energy Levels: Regular physical activity can boost your overall energy levels and stamina. Feeling more energetic can encourage you to stay active and maintain a healthier lifestyle.
To reap these benefits, aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise per week, along with strength training exercises at least twice a week. Always consult with your healthcare provider before starting a new exercise program, especially if you have existing health concerns. Remember, incorporating exercise into your daily routine can be enjoyable—whether it’s walking, dancing, swimming, or any other activity that gets your heart rate up!
Seeking Professional Medical Help
When it comes to managing diabetes and preventing complications such as amputations, seeking professional medical help is paramount. Knowing when and how to reach out to healthcare providers can significantly impact your health outcomes. Here’s why professional guidance is essential:
1. Comprehensive Care: Healthcare professionals, including endocrinologists, dietitians, and podiatrists, can offer a holistic approach to managing diabetes. They can provide tailored treatment plans that address your unique needs, helping you achieve better control of your condition.
2. Regular Monitoring: Regular check-ups are crucial for monitoring your diabetes management. Professionals can conduct blood tests, assess your overall health, and make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan based on your current health status.
3. Early Detection of Problems: Doctors can identify potential complications early, including issues related to your feet, kidneys, and cardiovascular system. Early intervention can prevent minor issues from escalating into serious conditions that could lead to amputations or other severe complications.
4. Education and Resources: Professional healthcare providers can educate you about diabetes management, including diet, exercise, and foot care. They can also recommend resources such as diabetes management programs or support groups that can help you along your journey.
5. Medication Management: Proper medication is essential for controlling blood sugar levels. Healthcare professionals can monitor your medication regimen, adjusting dosages as needed to ensure you are receiving the most effective treatment.
6. Emotional and Psychological Support: Living with diabetes can be emotionally challenging. Healthcare providers can connect you with mental health professionals or diabetes support groups that can provide the emotional support and coping strategies needed to manage the psychological aspects of the disease.
In summary, don’t hesitate to seek professional medical help. Whether you’re newly diagnosed or have been managing diabetes for years, maintaining regular communication with your healthcare team is vital for successfully managing your condition and preventing complications. When it comes to your health, being proactive is the key!
Conclusion
Managing diabetes effectively requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates various elements, such as proper diet, regular exercise, vigilant foot care, and professional medical support. By understanding diabetes and its complications, recognizing the signs of potential foot problems, and fostering good habits, you can greatly reduce the risk of serious complications like amputations.
Remember, your diet is a powerful tool for controlling blood sugar levels, while exercise enhances your overall health and well-being. Regular foot care and monitoring are essential practices that can help catch issues early, allowing for timely intervention.
Finally, never underestimate the importance of seeking professional medical help. Building a supportive healthcare team can provide you with tailored guidance, regular assessments, and crucial emotional support. By taking these proactive steps, you empower yourself to lead a healthier life and manage your diabetes effectively. Your feet—and your future—will thank you!
FAQ – Common Questions About Diabetes Management
What are the signs that I should watch for regarding diabetic foot problems?
Look for numbness, tingling, sores that don’t heal, redness, swelling, and changes in skin color or texture.
How can a healthy diet help manage diabetes?
A healthy diet helps control blood sugar levels, maintain a healthy weight, and provides essential nutrients that support overall health.
What types of exercise are beneficial for diabetes management?
Both aerobic exercises, like walking and swimming, and strength training can improve insulin sensitivity and overall health.
Why is regular foot care important for diabetics?
Regular foot care helps detect problems early, prevents wounds and infections, and promotes overall foot health.
How often should I see my healthcare provider for diabetes management?
It’s recommended to see your healthcare provider at least every three to six months, but you may need to visit more frequently based on your individual condition.
What should I do if I have a foot injury as a diabetic?
Seek medical attention promptly, especially if the injury does not heal or shows signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or pus.